- Home
- Binder Jetting Resources
- Blog
Koszalin University of Technology Relies on a Metal 3D Printer from ExOne
Koszalin University of Technology Relies on a Metal 3D Printer from ExOne

Koszalin University of Technology Relies on a Metal 3D Printer from ExOne
Koszalin University of Technology Relies on a Metal 3D Printer from ExOne
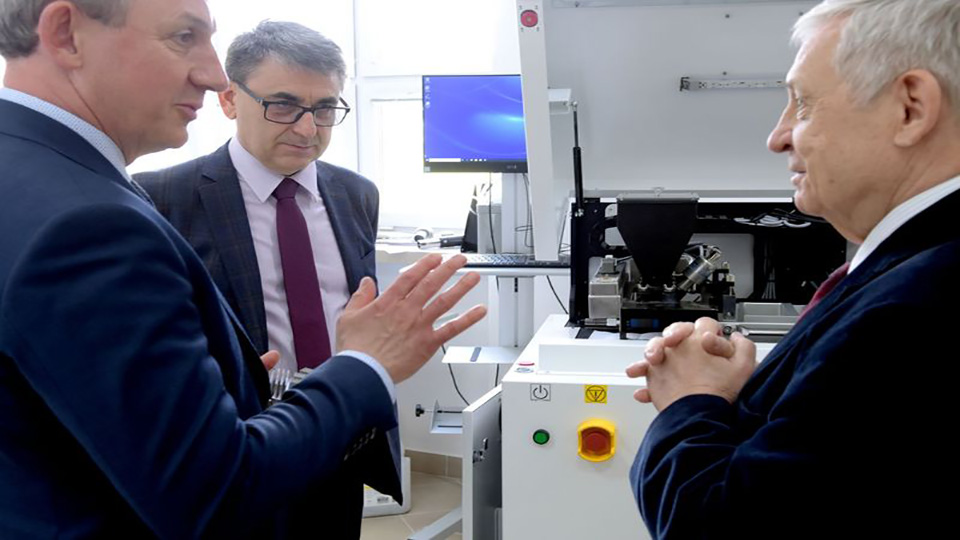
The Koszalin University of Technology is the second educational institute in Poland to procure a 3D printer with a metal binder jetting system from ExOne, with an Innovent+ being installed in the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering in June 2020. The 3D printer will allow students to research additive manufacturing and discover the potential this technology harbors. The machine will also be used to support local companies and show them the advantages of additive manufacturing. “I have been following the development of the binder jetting technology for several years now, and based on its potential and the diverse application areas, I decided to invest in such a machine for our new research center,” said Prof. Błażej Bałasz, Professor at the faculty.
How the binder jetting process works
The Innovent+ uses ExOne’s patented binder jetting technology, an additive procedure which uses a liquid binding agent that is selectively applied to powder particles. The material is thereby joined together, becoming an object layer by layer. Following the printing process, excess material is removed and the object is post-processed – in the case of metal 3D printing, the printed part is sintered in a special oven at high temperatures.
University research center for additive manufacturing procedures
The Innovent+ is part of a cutting-edge research center. At the Faculty for Mechanical Engineering at the Koszalin University of Technology, students are researching innovative methods for manufacturing machine parts. To further expand this area of research, the faculty implemented the “Rapid Prototyping Center” project: The research center is equipped with high-tech devices to research additive manufacturing technologies. Among other devices, the center has a laser scanner which digitizes objects precisely and quickly, thereby enabling the creation of digital models. The center also has a unique device for manufacturing metal powders under laboratory conditions, as well as an inspection machine for testing the strength and wear-resistance of the parts.
Two metal 3D printers are at the heart of the center, with each deploying a different production method: One device uses a laser sintering method, while the other is ExOne’s Innovent+ printer. The faculty is currently using the Innovent+ to research 316L metal powder, with plans in place to use other alloys, such as 17-4PH, copper and tool steel in the future. “There is a fascinating journey ahead of us, full of research and development work, on which we will accompany our students,” said Prof. Błażej Bałasz.
Additive manufacturing enables design without limits
The Koszalin University of Technology hopes to use the Innovent+ and the entire research center to show industrial companies in the region the benefits of additive manufacturing. These additive processes allow a completely new approach when it comes to designing machine parts, as they enable extraordinary design freedom compared to traditional manufacturing processes. Even complex shapes with different properties can be manufactured easily and quickly using this approach. “Until now, our options were limited by the shape of the tools used to manufacture the part. Additive manufacturing circumvents these restrictions,” explained Prof. Błażej Bałasz.
In the future, the Faculty for Mechanical Engineering aims to enter into various collaborations with local companies, with other practical research projects planned within this scope. As a pioneer in the area of metal 3D printing technology, the Koszalin University of Technology hopes to provide impetus for the innovative and pioneering manufacturing process.
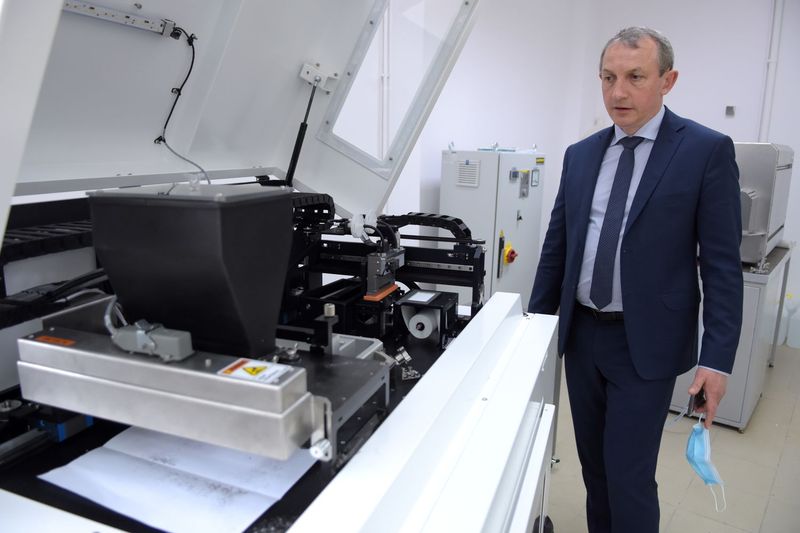 Błażej Bałasz, BEng, PhD, DSc
Błażej Bałasz, BEng, PhD, DSc
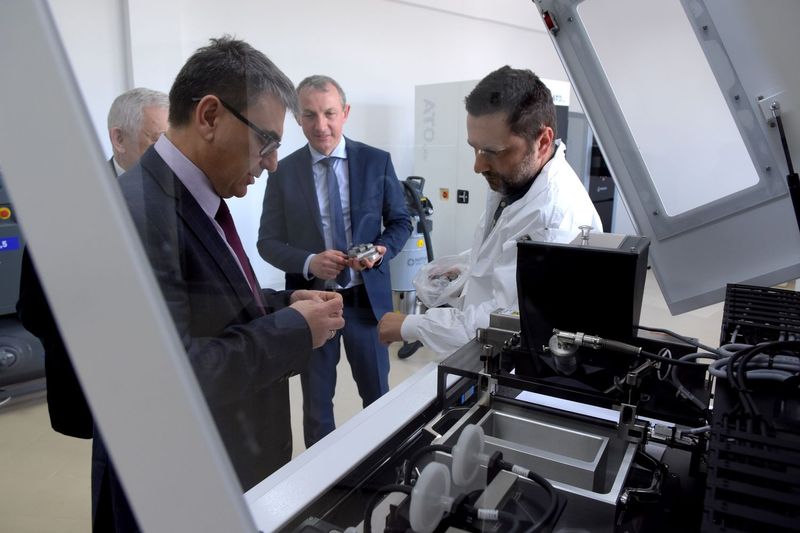 From left:
From left:
Waldemar Kuczyński, BEng, PhD, DSc
Błażej Bałasz, BEng, PhD, DSc
Tomasz Szatkiewicz, BEng, PhD ExOne Innovent+
ExOne Innovent+
Metal 3D printer at Universiy of Technology in Koszalin, Poland


.PNG?ext=.png)









